In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, customers expect more than just a personalized experience—they demand hyper-personalization. As businesses grapple with increasing competition and ever-evolving customer expectations, the need to stand out has never been greater. Enter hyper-personalization, a strategy that leverages advanced data analytics, AI, and real-time customer insights to create truly individualized experiences that resonate with each consumer on a personal level.
What is Hyper Personalization in AI?
Hyper personalization refers to the advanced level of customization and tailoring of products, services, or experiences to individual customers, made possible by leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies. It goes beyond traditional personalization methods, which typically rely on broad segments or user profiles, by dynamically adapting and optimizing content, recommendations, and interactions in real-time based on individual preferences, behaviors, and contexts.
AI plays a crucial role in enabling hyper personalization by processing vast amounts of data from various sources, including browsing history, purchase patterns, social media interactions, and even real-time location or sensor data. Through machine learning algorithms, AI systems can identify intricate patterns, correlations, and insights that would be nearly impossible for humans to discern manually. This allows for a granular understanding of each individual’s unique preferences, interests, and behaviors, enabling highly tailored experiences.
Unlike traditional personalization, which relies on predefined rules or segments, hyper personalization is dynamic and adaptive. It continuously learns and refines its understanding of individual users, adjusting recommendations, content, and experiences accordingly. This level of personalization is particularly valuable in industries such as e-commerce, media and entertainment, and customer service, where delivering highly relevant and engaging experiences can significantly impact customer satisfaction, loyalty, and revenue.
The Rise of Hyper Personalization
The demand for hyper personalization has been steadily rising due to several key factors. First and foremost, consumer expectations have evolved significantly in the digital age. Customers now expect tailored experiences that cater to their unique preferences, interests, and behaviors. They are no longer satisfied with generic, one-size-fits-all offerings, as they have grown accustomed to the personalized recommendations and experiences provided by companies like Amazon, Netflix, and Spotify.
Secondly, the competitive landscape has become increasingly fierce, with businesses vying for customer attention and loyalty. Hyper personalization has emerged as a powerful differentiator, enabling companies to stand out from the competition by delivering highly relevant and engaging experiences. By leveraging data and AI to understand customers on a granular level, businesses can create personalized interactions that resonate with individuals, fostering stronger connections and driving customer loyalty.
AI Techniques for Hyper Personalization
Hyper personalization relies on advanced AI techniques to analyze vast amounts of data and deliver tailored experiences. Several key AI technologies drive hyper personalization efforts:
Machine Learning Algorithms: Machine learning models are at the core of hyper personalization. These algorithms can identify patterns, make predictions, and continuously learn from new data. Techniques like collaborative filtering, content-based filtering, and hybrid approaches are used to recommend personalized content, products, or services based on user preferences and behavior.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP algorithms enable machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. In hyper personalization, NLP is used to analyze customer interactions, such as chat logs, emails, and social media posts, to gain insights into their interests, sentiments, and preferences. This information can then be used to provide personalized responses, recommendations, and content.
Computer Vision: Computer vision techniques allow machines to interpret and analyze visual data, such as images and videos. In hyper personalization, computer vision can be used to recognize products, objects, and scenes in user-generated content or product catalogs, enabling personalized recommendations and targeted advertising based on visual preferences.
Data Mining: Data mining techniques are used to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships within large datasets. In hyper personalization, data mining algorithms can identify customer segments, behavior patterns, and preferences by analyzing structured and unstructured data from various sources, such as purchase histories, browsing data, and social media activity.
Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics uses statistical models and machine learning techniques to make predictions about future events or behaviors. In hyper personalization, predictive analytics can be used to anticipate customer needs, preferences, and behavior, enabling proactive and personalized recommendations, offers, and experiences.
By combining these AI techniques, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their customers, enabling them to deliver highly personalized and relevant experiences across various touchpoints, such as websites, mobile apps, and in-store interactions.
Data and Hyper Personalization
Data plays a crucial role in enabling hyper personalization through AI. Without access to relevant and high-quality data, it would be impossible to understand individual preferences, behaviors, and contexts to deliver truly personalized experiences. The effectiveness of hyper personalization is directly proportional to the quality and quantity of data available.
Importance of Data
Data is the fuel that powers hyper personalization engines. It provides insights into customer behavior, preferences, interests, and patterns, allowing AI algorithms to learn and make accurate predictions. The more data available, the better the algorithms can identify patterns and tailor experiences to each individual.
Types of Data Used
Various types of data are used for hyper personalization, including:
- Behavioral Data: This includes data about user interactions, browsing history, purchase history, and engagement with content or products.
- Contextual Data: This encompasses data about the user’s location, device, time of day, weather conditions, and other contextual factors that can influence preferences.
- Demographic Data: This includes information about the user’s age, gender, income level, education, and other demographic characteristics.
- Psychographic Data: This involves data about the user’s personality traits, values, interests, and lifestyles.
Data Collection Methods
Data can be collected from various sources, including:
- User Interactions: Data is gathered from user interactions with websites, mobile apps, and other digital platforms.
- Surveys and Feedback: Direct feedback from users through surveys, reviews, and ratings can provide valuable insights.
- Social Media: Data from social media platforms, such as preferences, interests, and connections, can be leveraged.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Devices: Connected devices, such as wearables and smart home devices, can provide data about user behavior and preferences.
Data Privacy and Ethical Considerations
While data is essential for hyper personalization, it is crucial to address data privacy and ethical concerns. Businesses must ensure they comply with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Transparent data collection practices, user consent, and secure data handling are essential.
Additionally, ethical considerations must be taken into account to avoid potential biases, discrimination, and misuse of personal data. Responsible AI practices, including algorithmic fairness, explainability, and accountability, should be implemented to ensure hyper personalization is used ethically and for the benefit of users.
Applications of Hyper Personalization in Various Industries
E-commerce: Hyper personalization in e-commerce involves tailoring product recommendations, search results, and promotions to individual customers based on their browsing history, purchase patterns, and preferences. Online retailers like Amazon and Netflix use AI algorithms to analyze customer data and provide highly personalized shopping experiences, increasing customer satisfaction and sales.
Marketing: AI-powered hyper personalization in marketing enables companies to deliver targeted advertisements, email campaigns, and content to specific segments or individual customers based on their interests, demographics, and behavior. This approach improves engagement, conversion rates, and overall marketing effectiveness.
Content Delivery: Streaming platforms, news websites, and social media feeds leverage hyper personalization to curate and serve content tailored to each user’s preferences, interests, and consumption patterns. AI algorithms analyze user data and interactions to provide a highly personalized content experience, increasing engagement and user satisfaction.
Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide hyper personalized customer service by understanding individual customer preferences, purchase history, and context. This allows for more efficient and personalized support, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, hyper personalization can be applied to personalize treatment plans, medication dosages, and preventive care recommendations based on individual patient data, such as medical history, genetics, and lifestyle factors. This approach enables more precise and effective healthcare delivery.
Education: AI-driven hyper personalization in education can adapt learning materials, pace, and teaching methods to individual student needs, learning styles, and progress. Personalized learning experiences can improve student engagement, comprehension, and academic performance.
These are just a few examples of how hyper personalization powered by AI is being applied across various industries to enhance customer experiences, improve efficiency, and drive better outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of Hyper Personalization
Hyper personalization, while offering significant benefits, also presents several challenges and limitations that must be addressed. These include:
Data Quality and Quantity Issues: Hyper personalization relies heavily on the availability of high-quality and diverse data. Incomplete, inaccurate, or biased data can lead to flawed personalization models and inaccurate recommendations or experiences. Additionally, obtaining sufficient data to effectively personalize for every individual can be a significant challenge, especially for smaller organizations or niche industries.
Algorithmic Bias: The algorithms used for hyper personalization can inadvertently perpetuate biases present in the training data or introduce new biases due to their design or implementation. This can result in unfair or discriminatory personalization, which can have serious ethical and legal implications.
Privacy Concerns: Hyper personalization often requires collecting and processing large amounts of personal data, which raises privacy concerns. Consumers may be hesitant to share their data or may feel that their privacy is being violated, leading to a loss of trust in the organization. Compliance with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, is also a critical consideration.
Technological Complexity: Implementing hyper personalization at scale requires sophisticated technologies, including machine learning algorithms, big data processing, and real-time personalization engines. Managing and integrating these technologies can be complex and resource-intensive, particularly for organizations without the necessary technical expertise or infrastructure.
Cost Considerations: Developing and maintaining hyper personalization systems can be costly, requiring significant investments in data acquisition, storage, processing, and analysis, as well as specialized personnel and infrastructure. The return on investment may not be immediately apparent, particularly for smaller organizations or those in highly competitive markets.
Organizations must carefully weigh the benefits of hyper personalization against these challenges and limitations. Addressing data quality and quantity issues, mitigating algorithmic bias, ensuring privacy compliance, managing technological complexity, and justifying the associated costs are critical for successful implementation and adoption of hyper personalization strategies.
The Future of Hyper-Personalization
As technology continues to evolve, the possibilities for hyper-personalization are virtually limitless. In the future, we can expect even more sophisticated AI algorithms, better data integration, and more seamless customer experiences. Businesses that embrace hyper-personalization today will be well-positioned to thrive in this rapidly changing landscape.
Hyper-personalization is not just a trend—it’s the future of digital marketing. By leveraging the power of data, AI, and real-time insights, you can create personalized experiences that drive customer loyalty, increase conversions, and ultimately, fuel business growth. Start implementing hyper-personalization in your digital marketing strategy today and unlock the full potential of your customer relationships.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Netflix’s Personalized Recommendations
Netflix’s data-driven approach to personalized content recommendations has been a game-changer in the entertainment industry. By leveraging advanced AI algorithms and analyzing user behavior patterns, Netflix can suggest shows and movies tailored to individual preferences with remarkable accuracy. This hyper-personalization strategy has not only enhanced user engagement but also contributed to Netflix’s massive subscriber growth and retention.
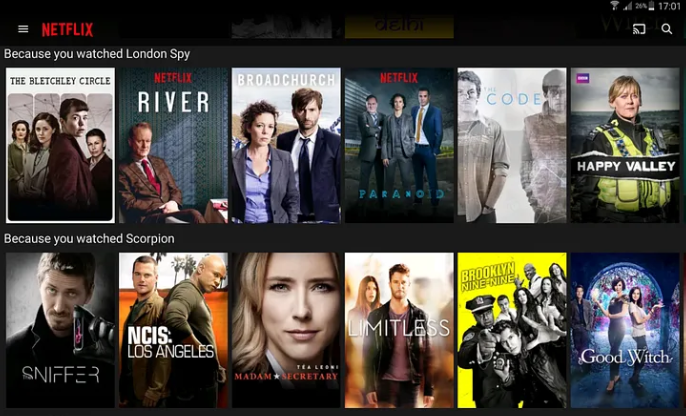
Image source
Amazon’s Personalized Shopping Experience
Amazon is a pioneer in hyper-personalization, offering a highly customised shopping experience to its customers. By analyzing browsing history, purchase data, and preferences, Amazon’s AI system provides personalized product recommendations, tailored search results, and even personalized pricing strategies. This level of personalization has significantly increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and sales for the e-commerce giant.
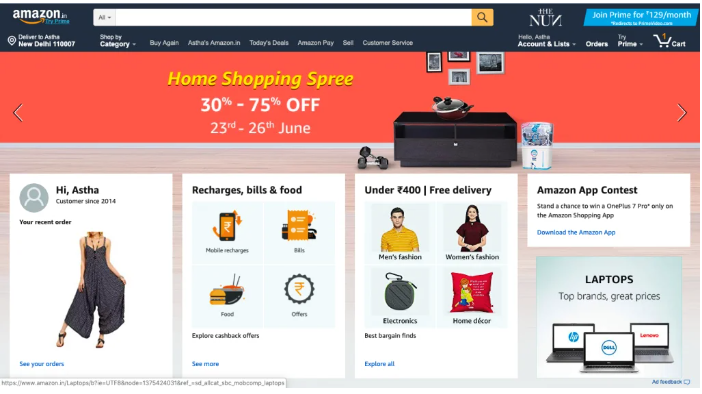
Image source
Stitch Fix’s AI-Powered Personal Styling
Stitch Fix, an online personal styling service, has embraced hyper-personalization by using AI to curate personalized clothing selections for its customers. By analyzing data from style quizzes, feedback, and past purchases, Stitch Fix’s algorithms can predict individual fashion preferences with remarkable accuracy. This hyper-personalized approach has disrupted the fashion industry and created a loyal customer base for the company.
Spotify’s Personalized Music Recommendations
Spotify’s music streaming platform has mastered hyper-personalization through its Discover Weekly and Release Radar features. By analyzing users’ listening habits, musical preferences, and contextual data, Spotify’s AI algorithms can recommend new and personalized music tailored to individual tastes. This hyper-personalization strategy has contributed to Spotify’s success in retaining users and increasing engagement.
Lessons Learned
These case studies highlight the transformative power of hyper-personalization and the potential it holds for businesses across various industries. However, successful implementation requires a deep understanding of customer data, effective data management practices, and a commitment to continuous improvement and adaptation. Companies must also prioritize data privacy and transparency to maintain consumer trust.
Best Practices for Implementing Hyper Personalization
Implementing hyper personalization effectively requires a strategic approach to data collection, management, and analysis, as well as careful selection of AI tools and techniques. Here are some best practices to consider:
Strategies for Data Collection and Management
- Collect data from multiple sources, including customer interactions, online behavior, and third-party data providers.
- Implement robust data governance policies to ensure data quality, privacy, and security.
- Invest in data management systems that can handle large volumes of structured and unstructured data.
- Regularly clean and preprocess data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Selecting the Right AI Tools and Techniques
- Evaluate various AI algorithms and techniques, such as machine learning, natural language processing, and deep learning, to determine the most suitable approach for your use case.
- Consider the scalability and performance requirements of your hyper personalization solutions.
- Leverage cloud-based AI platforms and services to reduce infrastructure costs and gain access to the latest technologies.
- Continuously monitor and update your AI models to ensure they remain accurate and relevant.
Testing and Optimization
- Implement A/B testing and multivariate testing to evaluate the effectiveness of your hyper personalization strategies.
- Continuously monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and user feedback to identify areas for improvement.
- Iteratively refine your AI models and personalization algorithms based on testing results and user behavior.
- Encourage a culture of experimentation and data-driven decision-making within your organization.
User Experience Considerations
- Prioritize transparency and user control over personalization settings and data usage.
- Ensure personalized experiences are seamless and intuitive, without overwhelming or confusing users.
- Strike a balance between personalization and privacy, respecting user preferences and consent.
- Continuously gather user feedback and incorporate it into your personalization strategies.
By following these best practices, organizations can effectively implement hyper personalization, leveraging the power of AI while delivering exceptional user experiences and maintaining trust and transparency.
